Have you ever wondered how volcanic eruptions shape the earth’s landscape and impact our climate? In a recent seabed survey around the Kikai caldera in Japan, scientists identified the biggest Holocene volcano eruption ever recorded. This monumental event took place approximately 7,300 years ago and has provided insights into the dynamics of volcanic mega events and their far-reaching consequences. Let’s delve deeper into the findings of this groundbreaking study together!
Uncovering the Biggest Holocene Volcano Eruption
The seabed survey conducted around the Kikai caldera in Japan revealed the largest volcano eruption of the Holocene period, which occurred around 7,300 years ago. This discovery has significant implications for our understanding of volcanic activity and its impact on the environment and human history.
Seismic Imaging and Sediment Sampling
To uncover the details of this historic eruption, the research team utilized seismic imaging and sediment sampling techniques. These methods allowed scientists to visualize the structure of the volcano beneath the seabed and analyze the layers of sediment deposited by the eruption.
By examining the seismic data and sediment samples collected from the site, researchers were able to reconstruct the sequence of events that led to the massive eruption. This information helped them understand the magnitude of the eruption and its impact on the surrounding environment.
Ejection of Volcanic Products
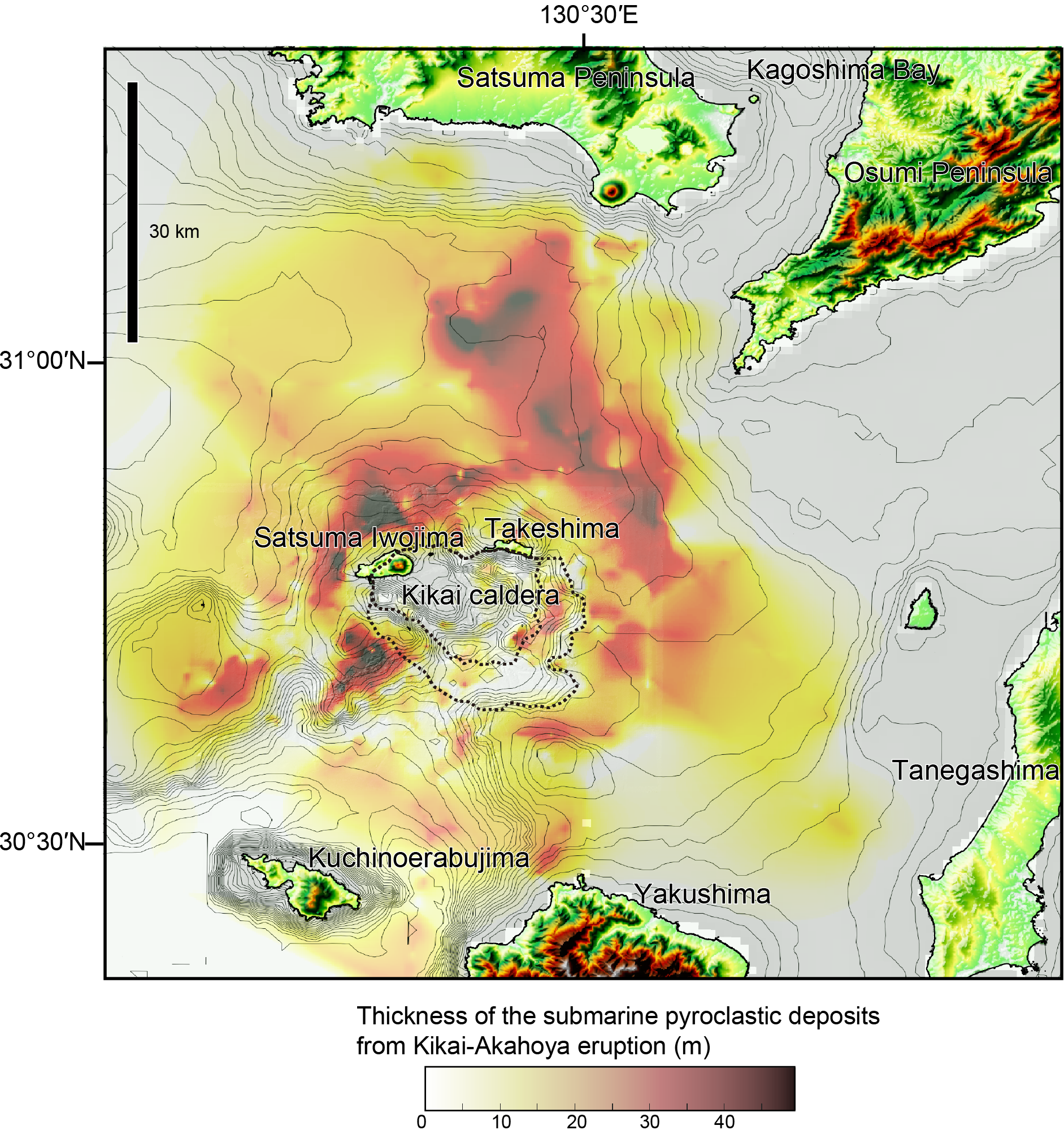
The Kikai caldera eruption resulted in the ejection of large amounts of volcanic products, including ash, rock fragments, and lava. These materials were dispersed over an area of approximately 4,500 square kilometers, covering the surrounding landscape with a thick layer of volcanic debris.
The study of these volcanic products has provided valuable insights into the intensity of the eruption and the volume of material expelled from the volcano. By analyzing these materials, scientists can estimate the scale of the eruption and its potential impact on the environment and climate.
This image is property of www.kobe-u.ac.jp.
Understanding the Impact of Volcanic Mega Events
The discovery of the largest Holocene volcano eruption has shed light on the dynamics of volcanic mega events and their consequences for the earth’s climate and history. Understanding the impact of these massive eruptions is crucial for predicting and preparing for future volcanic events.
Climate Effects
Volcanic eruptions can have a significant impact on the earth’s climate, both in the short and long term. The release of volcanic gases and particulates into the atmosphere can lead to the formation of sulfuric acid aerosols, which can cause cooling of the earth’s surface.
These aerosols can reflect sunlight back into space, reducing the amount of solar radiation reaching the earth and resulting in lower temperatures. This cooling effect can persist for several years after a major volcanic eruption, affecting global climate patterns and weather systems.
Environmental Consequences
In addition to their impact on climate, volcanic mega events can have significant environmental consequences. The deposition of volcanic ash and debris can alter the landscape, burying vegetation and altering ecosystems.
The release of toxic gases during an eruption can also pose a threat to human health and wildlife. By studying the aftermath of past volcanic events, scientists can better understand the potential hazards associated with future eruptions and develop strategies to mitigate their impact on the environment.
Historical Significance
The study of volcanic mega events like the Kikai caldera eruption is not only important for understanding their impact on the environment but also for illuminating their role in shaping human history. Throughout history, volcanic eruptions have played a significant role in shaping the course of civilizations and influencing cultural development.
The devastation caused by volcanic eruptions has been recorded in historical texts and archaeological evidence, providing valuable insights into the effects of these natural disasters on human societies. By studying the largest Holocene volcano eruption and its aftermath, scientists can gain a better understanding of how past civilizations coped with and adapted to environmental challenges.

This image is property of www.geologypage.com.
Implications for Future Research and Preparedness
The discovery of the biggest Holocene volcano eruption has significant implications for future research and preparedness efforts aimed at reducing the impact of volcanic eruptions on society and the environment. By studying past mega events, scientists can better understand the mechanisms that drive volcanic activity and develop strategies to monitor and mitigate volcanic hazards.
Predicting Future Eruptions
One of the key goals of studying past volcanic eruptions is to develop methods for predicting future events. By analyzing the geological record of past eruptions, scientists can identify patterns and trends that may signal the onset of a volcanic eruption.
These findings can be used to develop early warning systems and evacuation plans for at-risk areas, helping to minimize the impact of future eruptions on human populations. Understanding the factors that contribute to volcanic activity is essential for improving our ability to predict and respond to volcanic hazards.
Monitoring Volcanic Activity
Advances in technology have made it possible to monitor volcanic activity in real-time, providing valuable data that can help scientists predict and prepare for eruptions. By using tools such as seismic monitoring, gas analysis, and satellite imaging, researchers can track changes in volcanic behavior and alert authorities to potential threats.
Continuous monitoring of active volcanoes is essential for early detection of signs of an impending eruption and for assessing the risk to surrounding communities. By combining field observations with advanced monitoring techniques, scientists can gather data to improve our understanding of volcanic processes and increase our ability to respond to volcanic emergencies.
Enhancing Preparedness and Resilience
The findings of the largest Holocene volcano eruption underscore the importance of enhancing preparedness and resilience in regions prone to volcanic activity. By developing comprehensive hazard mitigation plans and investing in infrastructure to withstand volcanic hazards, communities can reduce the risk of catastrophic events and minimize the impact of eruptions on human lives and property.
Educating the public about the dangers of volcanic eruptions and providing guidance on evacuation procedures can help communities prepare for potential emergencies. Building partnerships between scientists, government agencies, and the public is essential for improving communication and coordination in the event of a volcanic crisis.

This image is property of www.ecomagazine.com.
Conclusion
The discovery of the biggest Holocene volcano eruption around the Kikai caldera in Japan has provided valuable insights into the dynamics of volcanic mega events and their far-reaching consequences. By studying the details of this historic eruption, scientists have advanced our understanding of volcanic activity and its impact on the environment, climate, and human history.
Moving forward, continued research and monitoring of volcanic activity will be essential for improving our ability to predict and prepare for future eruptions. By leveraging technological advancements and interdisciplinary collaboration, scientists can work towards developing strategies to mitigate the impact of volcanic hazards on society and build resilience in at-risk communities.
As we continue to learn from the past and adapt to the challenges of the present, we can cultivate a deeper appreciation for the power and beauty of the earth’s natural forces. By embracing a spirit of curiosity and cooperation, we can navigate the complexities of our dynamic planet and strive towards a more sustainable and resilient future.
This image is property of www.kobe-u.ac.jp.
